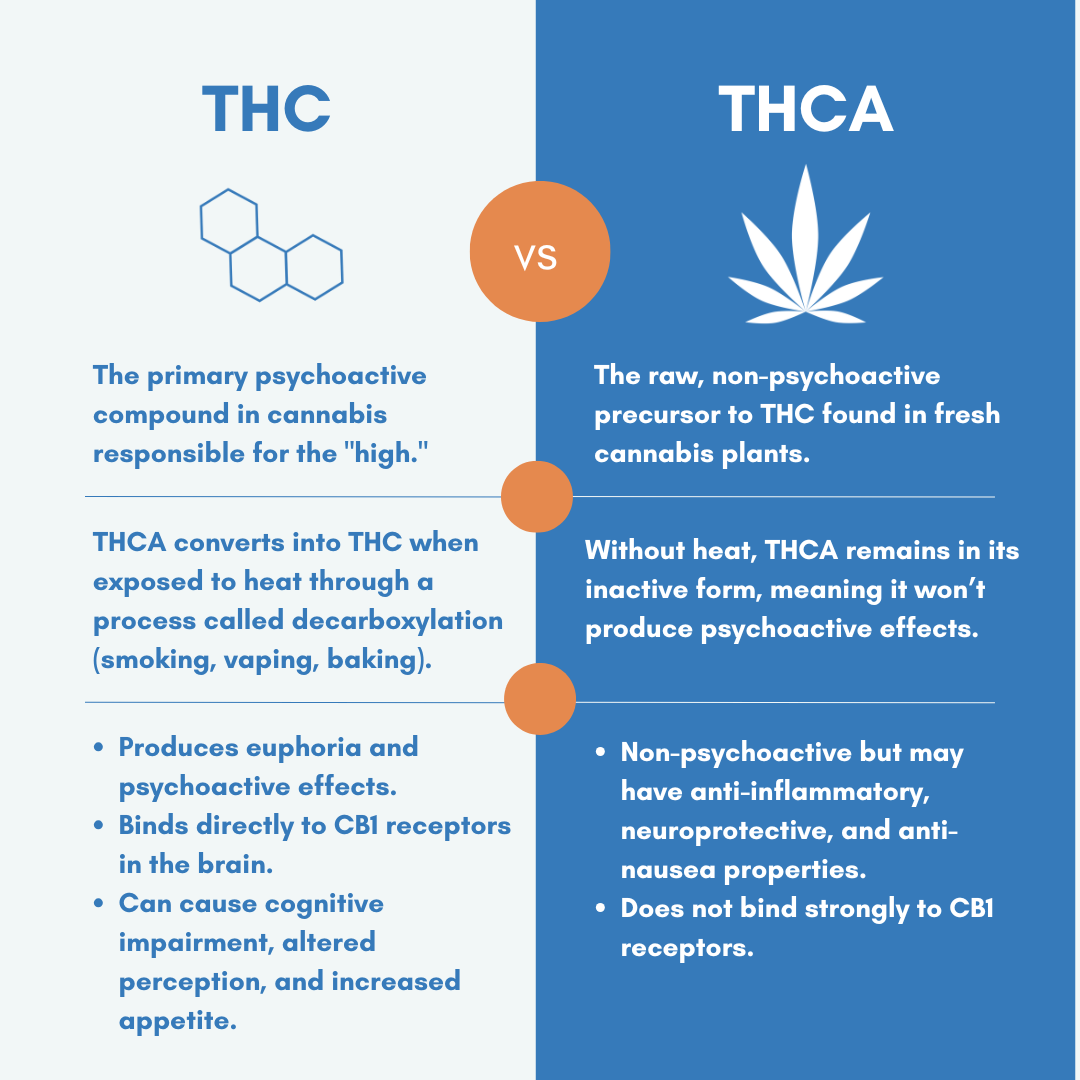
Cannabis, a plant known for its chemical diversity, contains essential cannabinoids like THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), each with distinct psychoactive properties and therapeutic potential. THC, the primary psychoactive compound, directly impacts the brain’s CB1 receptors, producing euphoria and altered perception. This psychoactive THC effect is a major consideration in addiction treatment, as high THC content increases the risk of dependency.
In contrast, THCA is a non-psychoactive precursor found in raw cannabis plants. It remains inactive until decarboxylation, a heat-driven process that converts THCA into THC. This key difference plays a crucial role in how cannabis affects the body and mind. Understanding these nuances helps inform the therapeutic strategies at Align Recovery Centers, where we focus on both cannabis education and marijuana addiction treatment.
While THC is widely used for its therapeutic benefits, it also poses risks. Research indicates that approximately 30% of marijuana users develop marijuana use disorder, with higher risks for those exposed to potent THC products at a young age. Align Recovery Centers addresses these challenges by providing evidence-based treatment programs and educating clients on cannabis consumption, including the differences between THCA flower, THC flower, and processed cannabis products.
Our approach combines personalized therapy with education on medical cannabis and potential health benefits of non-psychoactive cannabinoids like THCA products. By understanding the total THC in various cannabis products, individuals can make informed decisions about their cannabis use. At Align Recovery Centers, we emphasize long-term health and sustainable recovery, ensuring that every client receives the tools and support needed to navigate cannabis-related challenges effectively.
What is THCA?
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is a naturally occurring cannabinoid found in the trichomes of raw cannabis plants. Unlike THC, its psychoactive counterpart, THCA is non-psychoactive, meaning it does not produce the “high” typically associated with cannabis use. THCA remains in its acidic form in fresh cannabis and only converts to THC through decarboxylation—a heat-driven process that occurs during smoking, vaping, cooking, or prolonged curing of cannabis.
Potential Therapeutic Benefits of THCA
The growing scientific interest in THCA highlights its promising therapeutic properties. Preliminary research suggests that THCA may have:
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Potentially beneficial for managing conditions like arthritis and lupus.
- Anti-nausea properties: A study in rat models indicated that THCA might reduce nausea, with possible applications for human treatments.
- Neuroprotective benefits: Emerging research explores THCA’s role in protecting against neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
These attributes make THCA an attractive option for those seeking the medicinal benefits of cannabis without the intoxicating effects of THC. As a result, patients interested in natural remedies often turn to raw cannabis products or THCA isolates.
What is THC?
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, responsible for the euphoric and mind-altering effects commonly associated with marijuana use. THC interacts with the brain’s CB1 receptors, part of the endocannabinoid system—a network that regulates crucial physiological functions, including mood, memory, appetite, and pain perception.
How Does THC Affect the Body?
The effects of THC can vary widely depending on factors such as dosage, consumption method, genetic predisposition, and prior cannabis use. Common experiences include:
- Positive effects: Euphoria, relaxation, and heightened sensory perception.
- Negative effects: Anxiety, paranoia, impaired memory, and, in some cases, severe psychotic reactions.
Risks and Addiction Potential of THC
While THC offers therapeutic benefits, its addictive potential remains a significant concern. Research indicates that approximately 30% of marijuana users may develop some degree of marijuana use disorder, particularly with frequent use or early exposure to high-potency THC products. Symptoms of dependency can include cravings, withdrawal, and difficulty reducing consumption despite adverse consequences.
At Align Recovery Centers, we emphasize education about THC’s effects to help individuals make informed decisions. Our comprehensive addiction treatment programs address the physical and psychological challenges associated with THC dependence, providing personalized care to support lasting recovery.
Key Differences Between THCA and THC
While both THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) originate from the cannabis plant, they differ in significant ways:
Chemical Composition
- THCA (C₂₂H₃₀O₄) contains an extra carboxyl group (-COOH), making it a larger and non-psychoactive molecule.
- THC (C₂₁H₃₀O₂) is formed through decarboxylation, where the loss of the carboxyl group alters the compound’s structure, enabling it to bind to CB1 receptors and cause psychoactive effects.
Psychoactivity
- THCA is non-psychoactive and does not produce the “high” associated with cannabis use.
- THC is psychoactive, binding to CB1 receptors in the brain, leading to euphoria, relaxation, and altered perception.
State in the Cannabis Plant
- THCA is the precursor to THC, naturally found in raw cannabis and THCA flower.
- THC forms only after decarboxylation, where heat (smoking, vaping, or cooking) converts THCA into THC.
Medical & Therapeutic Potential
- THCA has potential therapeutic benefits, including anti-inflammatory, anti-nausea, and neuroprotective properties.
- THC is used for pain relief, appetite stimulation, and treating conditions like PTSD, chronic pain, and insomnia.
Legal Status
- THCA products are often legally available because they do not contain psychoactive THC—until they undergo decarboxylation.
- THC products are regulated differently based on federal and state laws, with restrictions varying across the United States.
Consumption Methods
- THCA can be consumed through raw cannabis plant extracts, tinctures, or THCA isolates without inducing intoxication.
- THC is typically consumed by smoking, vaping, or ingesting edibles, which require heat to activate its psychoactive properties.
Understanding these key differences allows consumers and medical professionals to make informed decisions about cannabis consumption methods, therapeutic potential, and legal status. At Align Recovery Centers, we help individuals navigate the complexities of THCA vs THC, ensuring they choose the best approach for their health and recovery goals.
The Conversion Process: From THCA to THC
Decarboxylation is the key process through which THCA is converted into THC. This occurs when cannabis is exposed to heat, whether through smoking, vaping, or cooking. The process can also occur slowly when the plant material ages and is exposed to environmental factors. This conversion is critical for consumers who prefer the psychoactive effects of THC or for patients who might benefit from THC’s properties over those of THCA.
Health Risks and Safety
Consuming THC is not without risks, particularly in terms of psychological effects and the potential for dependence. In contrast, THCA is seen as potentially safer with fewer risks of psychoactive effects. However, users should always consider dosage and the method of consumption, as these can significantly influence the experience and safety of using cannabis products.
In recent years, there have been alarming reports of fentanyl-laced weed, which poses severe health risks. Fentanyl is an extremely potent synthetic opioid that is often mixed into other drugs to increase potency but can lead to accidental overdoses and severe health complications. At Align Recovery Centers, we are vigilant about this dangerous adulteration and strive to educate our community on the risks while providing support and treatment for those affected. Learn more about fentanyl in weed.
Treatment for Marijuana Addiction at Align Recovery Centers
Despite its popularity and increasing legal acceptance, marijuana can be addictive and may require professional treatment to overcome dependence. At Align Recovery Centers, we offer comprehensive marijuana addiction treatment programs that cater to the specific needs of our clients. These programs include both detoxification to manage withdrawal symptoms and ongoing therapy to address the psychological aspects of addiction.
Understanding the differences between THCA and THC is essential for anyone using cannabis, whether for medical or recreational purposes. By distinguishing the non-psychoactive properties of THCA from the psychoactive effects of THC, consumers can make better-informed decisions about their cannabis use. At Align Recovery Centers, we support individuals in making these decisions within the context of their overall health and wellness goals. If you or someone you know is struggling with substance use, particularly marijuana, we are here to help with resources, treatment, and ongoing support.

Elvis, a seasoned Licensed Clinical Social Worker and Clinical Director at Align Recovery Centers, brings over ten years of expertise in addiction therapy. Skilled in evidence-based therapies like CBT, DBT, and ACT, he specializes in creating personalized treatment plans for addiction and co-occurring mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. His holistic approach and dedication to his clients’ transformative journeys highlight his significant impact in addiction therapy and mental health care.